The Sneaky Culprits Behind Sinus Infections: A Comprehensive Guide
Sinus infection or sinusitis, is a common and often uncomfortable health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. While they can be quite bothersome, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you manage sinusitis effectively. In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve deep into sinus infection, exploring their underlying causes, the wide range of symptoms they present, and the various treatment options available to provide relief and promote recovery.
What is Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)?

Sinus infection, medically referred to as sinusitis, occur when the sinuses – air-filled spaces within the bones of the face and skull—become inflamed or infected. These infections can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including nasal congestion, facial pain, and headaches.
Sinusitis can be categorized into two main types:
-
Acute Sinusitis: This is a short-term condition that typically follows a cold or upper respiratory infection. It lasts for a brief period and often resolves with proper treatment.
-
Chronic Sinusitis: Chronic sinusitis persists for 12 weeks or longer, and it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It may require more extended treatment and management.
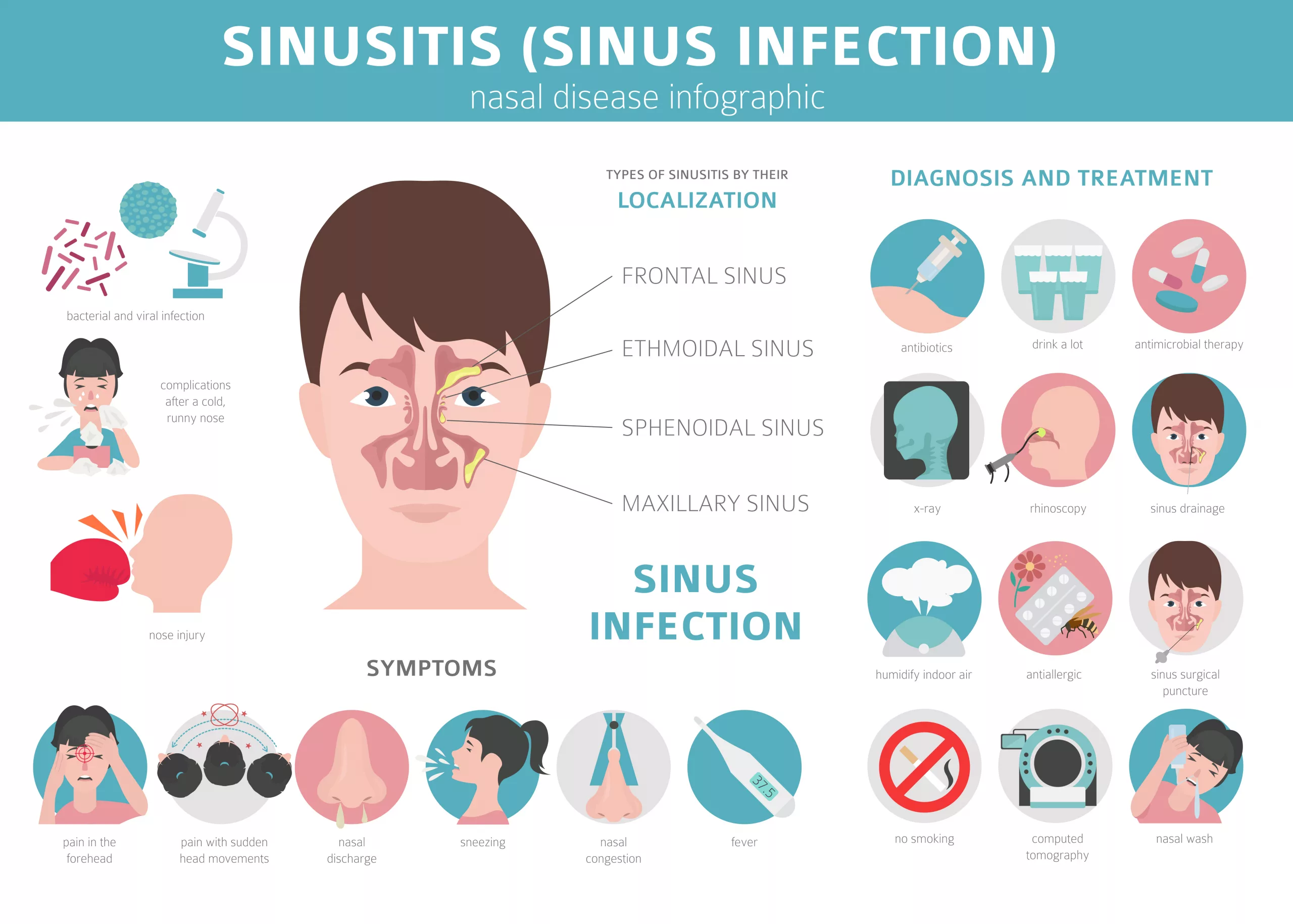
Anatomy of the Sinuses

Before we dive deeper into sinusitis, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of the sinuses. There are several sinus cavities located in the skull:
- Frontal sinuses: Positioned in the forehead area.
- Ethmoid sinuses: Located between the eyes and behind the nasal bridge.
- Maxillary sinuses: Found in the cheekbones.
- Sphenoid sinuses: Situated deep behind the nose.
These sinuses play a crucial role in regulating the flow of air, mucus, and bacteria in the nasal passages. When they become blocked or infected, it can result in sinusitis.
Causes of Sinus Infection
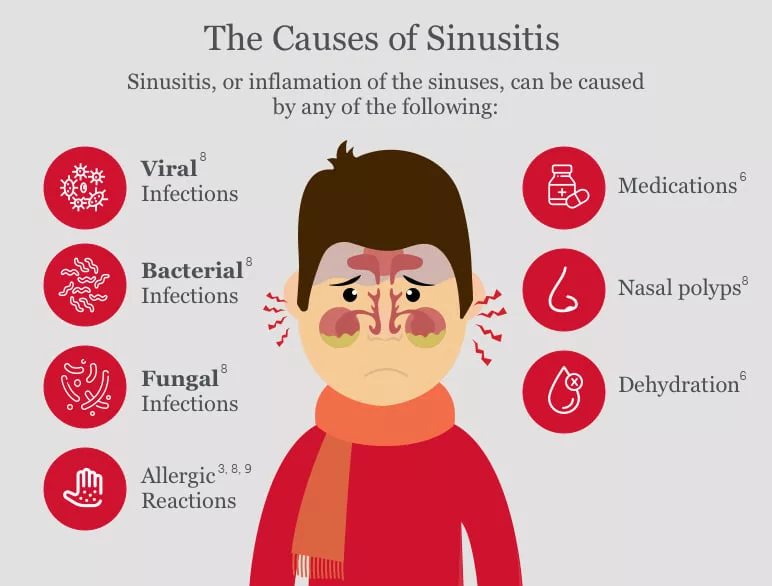
Understanding the causes of sinusitis is essential to effectively manage and prevent it. Several factors can contribute to the development of sinus infections:
-
Viral Infections
The common cold and influenza are common triggers of acute sinusitis. These viral infections can inflame the nasal passages and impair the normal functioning of the sinuses.
-
Bacterial Infections
While less common, bacterial infections can lead to acute sinusitis. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are common culprits.
-
Allergies
Allergic reactions to pollen, dust mites, animal dander, and other allergens can cause inflammation in the nasal passages, potentially leading to sinusitis.
-
Nasal Polyps
These noncancerous growths in the nasal passages can obstruct the flow of mucus and air, increasing the risk of sinus infections.
-
Deviated Septum
A deviated septum, a crooked or misaligned partition between the nostrils, can impede drainage from the sinuses and lead to recurrent sinusitis.
-
Respiratory Tract Infections
Infections of the respiratory tract, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, can sometimes spread to the sinuses.
-
Dental Issues
Dental problems, like infected teeth or gum disease, can cause sinusitis when the infection spreads to the sinuses.
Types of Sinus Infections

Sinus infections, medically known as sinusitis, can manifest in various forms depending on their duration and severity. Here are the main types of sinus infections:
-
Acute Sinusitis: This is the most common type of sinus infection. It usually occurs as a result of a viral upper respiratory infection, such as the common cold or the flu. Acute sinusitis is characterized by the sudden onset of symptoms and typically lasts for a short period, often a few days to a few weeks. It can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi.
- Chronic Sinusitis: Chronic sinusitis persists for an extended period, typically for 12 weeks or more. Unlike acute sinusitis, which is often triggered by infections, chronic sinusitis is often associated with other factors such as allergies, nasal polyps, or structural abnormalities in the nasal passages. It can be caused by a combination of factors, including bacterial or fungal infections.
- Subacute Sinusitis: Subacute sinusitis falls between acute and chronic sinusitis in terms of duration. It lasts longer than acute sinusitis but less than 12 weeks, typically spanning from 4 to 12 weeks. This type of sinusitis may be a transition phase between acute and chronic forms.
- Recurrent Sinusitis: Recurrent sinusitis is characterized by multiple episodes of acute sinusitis within a year. Individuals with recurrent sinusitis experience repeated bouts of sinus infections, which can be caused by various factors, including structural abnormalities in the nasal passages, allergies, or other underlying health conditions.
- Fungal Sinusitis: Fungal sinusitis is a less common but more severe type of sinus infection caused by fungal pathogens. It can affect both acute and chronic sinusitis and may require specific antifungal treatments. Fungal sinusitis is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS): AFS is a unique type of sinusitis that occurs in individuals with allergic reactions to fungal allergens. It can lead to chronic sinusitis and often presents with nasal polyps. Treatment involves addressing both the allergic component and fungal infection.
- Frontal Sinusitis: Frontal sinusitis specifically affects the frontal sinuses, which are located in the forehead area. Symptoms may include forehead pain, pressure, and discomfort. Treatment is similar to that of other sinus infections but may require specific attention to the frontal sinus area.
- Maxillary Sinusitis: Maxillary sinusitis targets the maxillary sinuses, which are located in the cheekbones. Symptoms include pain and pressure in the cheeks and upper teeth. It’s one of the most common types of sinusitis.
- Ethmoid Sinusitis: Ethmoid sinusitis affects the ethmoid sinuses, located between the eyes and behind the nasal bridge. Symptoms may include pain and pressure between the eyes and headaches. Ethmoid sinusitis can be challenging to treat due to its location.
-
Sphenoid Sinusitis: Sphenoid sinusitis is characterized by inflammation or infection of the sphenoid sinuses, located deep behind the nose. Symptoms may include deep headaches, neck pain, and discomfort behind the eyes. Sphenoid sinusitis is less common but can be more challenging to diagnose and treat due to its location.
It’s essential to recognize the type of sinusitis you may be experiencing to seek appropriate medical attention and treatment. Regardless of the type, sinus infections can cause discomfort and affect your daily life, so prompt diagnosis and management are crucial for relief and recovery.
Symptoms of Sinus Infection
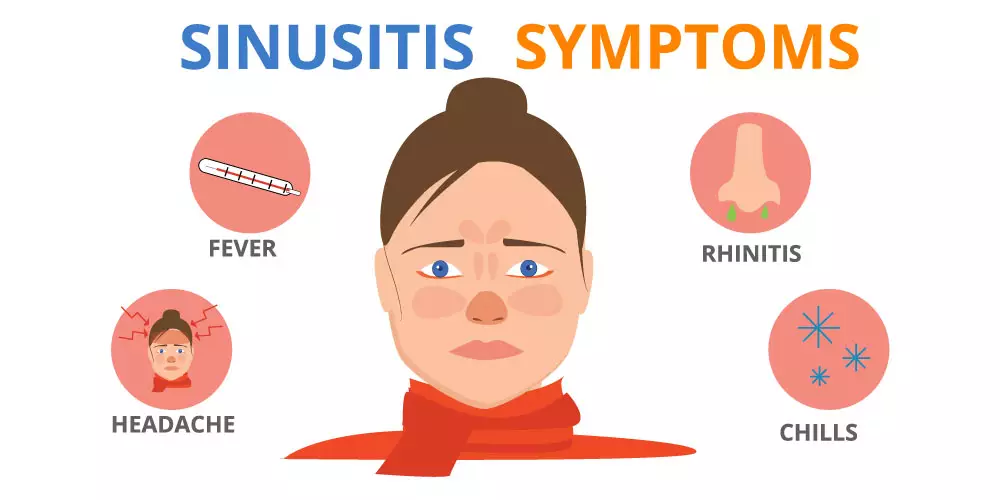
Sinus infection, also known as sinusitis, can cause a variety of symptoms, which can range from mild to severe. The specific symptoms and their severity can vary depending on the type of sinusitis (acute, chronic, etc.) and the underlying cause (viral, bacterial, or fungal). Here are common symptoms of a sinus infection:
-
Nasal Congestion: One of the hallmark symptoms of sinusitis is nasal congestion or a blocked nose. This occurs when the nasal passages become inflamed and swollen, making it difficult to breathe through the nose.
- Runny Nose: In addition to congestion, sinusitis often leads to a runny or dripping nose. The nasal discharge may be clear, thick, yellow, or green, depending on the cause of the infection.
- Facial Pain and Pressure: Many people with sinus infections experience facial pain, pressure, or discomfort. This pain is often concentrated in the forehead, between the eyes, or in the cheekbones.
- Headache: Sinus headaches are common and typically present as a constant, throbbing pain around the forehead, eyes, or cheekbones. These headaches can be quite painful and worsen with movement or bending over.
- Toothache: Sinus infections, especially those involving the maxillary sinuses (cheekbone area), can cause referred pain to the upper teeth.
- Reduced Sense of Smell and Taste: Sinusitis can lead to a loss or reduction in the sense of smell (anosmia) and taste (dysgeusia). This is often due to nasal congestion and inflammation.
- Coughing: Postnasal drip, which occurs when excess mucus flows down the back of the throat, can lead to a persistent cough. This cough is often worse at night.
- Sore Throat: The constant drainage of mucus into the throat can cause throat irritation and a sore throat.
- Fatigue: Dealing with the discomfort and symptoms of sinusitis can be exhausting, leading to feelings of fatigue and low energy levels.
- Fever: While not always present, acute bacterial sinusitis can lead to a low-grade fever.
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): The accumulation of mucus and bacteria in the sinuses can lead to bad breath.
- Ear Pressure or Fullness: Some individuals with sinusitis may experience ear symptoms, such as pressure, fullness, or even mild hearing impairment.
It’s important to note that the severity and duration of symptoms can vary from person to person. Additionally, some people may have more subtle or mild symptoms, while others may experience more severe discomfort. If you suspect you have a sinus infection, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Seeking Medical Help for Sinus Infection
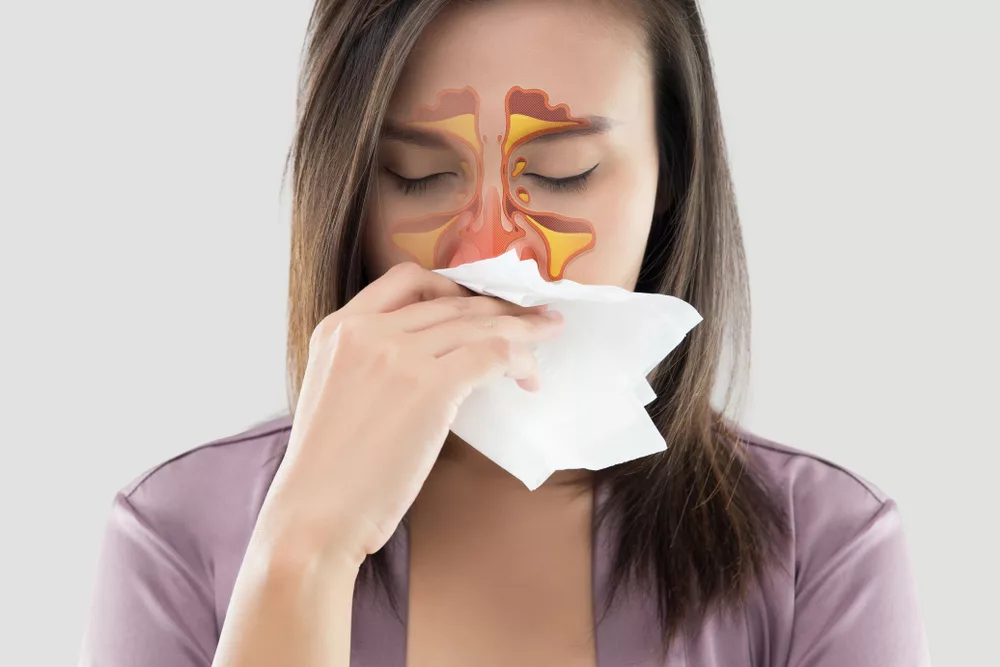

If you suspect you have a sinus infection or if your symptoms persist and worsen, it’s crucial to seek medical help. A healthcare provider can diagnose sinusitis through a physical examination and, if necessary, imaging studies like CT scans or nasal endoscopy.
In cases of acute bacterial sinusitis or severe symptoms, antibiotics may be prescribed. However, viral sinusitis typically resolves on its own, and treatment focuses on symptom relief.
For chronic or recurrent sinusitis, your healthcare provider may recommend a referral to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist or allergist to identify and address underlying causes such as allergies or structural abnormalities.
Sinus Infection Treatment
The treatment of a sinus infection, or sinusitis, depends on its type (acute or chronic) and its underlying cause (viral, bacterial, or fungal). Below, I’ll outline various treatment options commonly used for sinus infections:
Acute Sinusitis Treatment
Treatment for acute sinusitis often includes:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: These can help manage pain and reduce fever.
- Decongestants: Decongestants can alleviate nasal congestion.
- Saline nasal irrigation: This helps clear mucus and reduce inflammation.
- Steam inhalation: Inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water or using a humidifier can relieve congestion.
- Rest and hydration: Adequate rest and staying well-hydrated support the immune system in fighting off the infection.
Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial sinusitis, but they are not effective against viral infections. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
Chronic Sinusitis Treatment
Managing chronic sinusitis is more complex and may involve:
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays: These reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Allergy management: Identifying and managing allergens that trigger symptoms can be crucial.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots): Allergy-induced sinusitis may benefit from immunotherapy.
- Endoscopic sinus surgery: This may be necessary to remove nasal polyps or correct structural abnormalities.
- Treatment of underlying conditions: Addressing conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can help.
- Long-term antibiotic treatment: For recurring bacterial sinusitis, long-term antibiotic treatment may be recommended under medical supervision.
Home Remedies for Sinus Infection

In addition to medical treatment, several home remedies and self-care practices can help alleviate sinusitis symptoms and promote healing:
-
Nasal Irrigation
Using a saline nasal rinse or a Neti pot can help clear mucus and reduce congestion.
-
Steam Inhalation
Inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water or using a humidifier can provide relief from nasal congestion and discomfort.
-
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated thins mucus and supports the immune system.
-
Warm Compress
Applying a warm compress to the face can relieve facial pain and pressure.
-
Rest
Adequate rest allows the body to allocate energy to healing and recovery.
-
Avoid Triggers
If allergies are contributing to your sinusitis, minimizing exposure to allergens can help prevent flare-ups.
How to Prevent Sinus Infection?

Preventing sinus infections often involves taking measures to reduce risk factors and minimize exposure to potential causes. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Hand Hygiene
Regular handwashing with soap and water can help prevent the spread of viruses that can lead to sinus infections.
-
Avoid Close Contact
Steer clear of individuals who have respiratory infections, especially during cold and flu seasons.
-
Stay Current with Vaccinations
Receiving vaccinations for diseases like the flu can reduce your risk of developing sinusitis as a complication of these infections.
-
Manage Allergies
If allergies contribute to your sinusitis, consult with an allergist to identify and manage allergens that trigger your symptoms.
-
Humidify Your Home
Using a humidifier in your home can add moisture to the air, preventing dry nasal passages that can lead to sinusitis.
-
Practice Good Dental Hygiene
Maintaining oral health and addressing dental issues promptly can reduce the risk of dental infections spreading to the sinuses.
-
Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke
Smoking irritates the nasal passages and can make you more susceptible to sinus infections. Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke as well.
Conclusion: Sinus Infection

Sinus infection or sinusitis can range from a mild inconvenience to a chronic and debilitating condition. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management. While sinus infections themselves are not contagious, the conditions that can lead to sinusitis, such as viral respiratory infections, can be transmitted.
If you suspect you have a sinus infection or if your symptoms persist and worsen, seeking medical help is crucial. With the right diagnosis and treatment, you can relieve symptoms and prevent complications. Additionally, adopting preventive measures like hand hygiene, vaccinations, and managing underlying conditions can reduce the risk of sinus infections and promote overall well-being.
Florida Health Care | Best Healthcare Provider in Florida
Welcome to Florida Health Care. Best Healthcare Provider in Florida. Empowering Floridians to Make Informed Health Care Decisions. Florida Urgent Care Centers is dedicated to providing excellent healthcare and ensure best practice standards. We can provide medical assistance anytime you become sick or injured, if you are out of town and need a refill or when your regular doctor is not available for you immediately and you can’t wait for an appointment.
CALL NOW +1-888-306-9302
Is sinus a serious problem?
Most sinus infections last from a couple of days to a few weeks and are not a serious medical concern, but if left untreated, sinusitis can lead to further complications. These include nasal polyps, a deviated septum and serious allergies.
Can sinus be cured?
Permanent cures for chronic sinusitis and sinus headaches are sometimes possible, but it can depend on the reasons why you are affected. If your sinusitis is linked to allergies, then you can try allergy testing to find out the cause and then take steps to avoid the trigger.
Can I cure my own sinus infection?
Symptoms normally go away on their own within 10 days. OTC medications and natural remedies may help relieve your symptoms. If your symptoms last more than 10 days, talk with your doctor.
Can I eat banana in sinus?
Avoid dairy if you have had previous episodes of sinus infections. Also, try to avoid refined sugar as it is pro-inflammatory and increases the production of mucus. Other foods to avoid include tomatoes (contain histamines), chocolate, cheese, gluten, and fruits like bananas, which can cause congestion.
How long can sinus last?
An acute sinus infection lasts anywhere from ten days up to eight weeks. A chronic infection lasts even longer. It is ongoing - it may seem like it's improving, and then it comes right back as bad as it was at first. Chronic sinus infections may drag on for months at a time.


